Comprehensive Guide to Spider Identification in California


Intro
California is home to a vast range of spider species, each with its own unique characteristics and behaviors. The state's diverse ecosystems—from coastal regions to arid deserts—provide ideal habitats for spiders to thrive. Understanding these creatures goes beyond mere curiosity; it plays a vital role in appreciating the balance of our local ecosystems. In this guide, we’ll explore how to identify common spiders, their ecological contributions, and best practices for engaging with them safely.
As we dive into various sections, we’ll uncover practical identification techniques, habitats where these arachnids can be found, and tips on how to handle them without causing harm. You don’t need to be an expert to become familiar with the spiders that share your environment; with a little guidance, anyone can learn to recognize and respect these often-misunderstood animals.
Understanding the Importance of Spider Identification
Identifying spiders is not simply a task for entomologists or arachnologists, but rather a vital part of understanding our environment. Spiders, despite being often feared or misunderstood, play crucial roles in our ecosystems. By grasping the nuances of this topic, both casual observers and committed enthusiasts can appreciate these creatures' significance.
Ecological Role of Spiders
Spiders are more than just creepy crawlies lurking in the corners of our homes; they contribute markedly to ecological balance.
Predator-Prey Dynamics
When we talk about predator-prey dynamics, it’s like unraveling a delicate tapestry of life. Spiders sit right squarely at the center. They help keep pests at bay, making them essential allies in agriculture and gardening. By consuming insects, spiders reduce reliance on chemical pesticides. It’s a win-win. Less pesticide means a healthier environment and fewer chemicals washing into our water systems.
A critical aspect of predator-prey dynamics is the jelly-like silk that many spiders use to spin webs, which serve as traps. However, what sets predators apart is their adaptability. Some, like wolf spiders, hunt on foot without the aid of webs, displaying a diverse range of hunting strategies that can deter potential pests effectively. Understanding these dynamics enriches one’s appreciation of spiders and their pivotal roles in our ecosystem.
Biodiversity Indicators
Biodiversity indicators are nature’s telltale signs. Spiders, as ecological indicators, can reflect conditions in their environment. A diverse array of spider species often signals a healthy ecosystem. In areas where biodiversity is thriving, spider populations usually mirror the abundance and variety of other organisms. Learning how to identify various spider species becomes important not only for enthusiasts but also for conservation efforts.
Spiders are sensitive to changes in habitat. By keeping tabs on these creatures, researchers can gain insights into environmental health, especially as ecosystems face challenges from pollution and climate change. The unique feature of spiders as biodiversity indicators underscores the importance of their population dynamics and habitat requirements. But it’s not without challenges, as misidentification can lead to flawed conclusions about an ecosystem’s health.
Benefits of Identifying Spiders
Understanding spiders extends beyond the academic or environmental realms; it holds practical benefits for individuals and communities.
Mitigating Fear and Misunderstanding
Identifying spiders is key to dispelling myths and minimizing fear. Many people jump at the sight of a spider, often due to a lack of understanding. By learning to identify common species, people can distinguish between harmless and potentially dangerous spiders, such as the black widow.
One major benefit of this understanding is the reassurance it brings. Realizing that most spiders are non-toxic and actually beneficial can help shift perspectives and possibly foster a more harmonious relationship with them. However, the unique challenge lies in the widespread misinformation that often perpetuates fear, leading to unnecessary extermination.
Enhancing Garden Health
Identifying spiders also enhances garden health, a point that cannot be overstated for both novice and seasoned gardeners. Instead of seeing spiders as nuisances, gardeners can recognize them as nature's pest control agents. For example, orb-weavers may be spotted spinning intricate webs, catching flies and other pests. By learning to identify these helpful species, one can maintain a healthy, sustainable garden ecosystem.
The unique advantage here is the natural balance they bring to our gardens. By allowing spiders to thrive, gardens can flourish without excessive use of chemicals, promoting both plant health and biodiversity. However, it requires a bit of education and the willingness to appreciate these creatures as cohabitants of a thriving garden.
Key Characteristics of California Spiders
Understanding the key characteristics of spiders in California is essential for proper identification and appreciation of these arachnids. Each species presents unique features that contribute to its behavior, habitat preferences, and role in the ecosystem. By recognizing distinct physical and behavioral traits, enthusiasts can classify spiders more confidently and accurately. This knowledge not only aids in field identification but also serves a deeper purpose: fostering respect and understanding toward these often-misunderstood creatures.
Physical Traits
Body Structure
The body structure of spiders in California generally consists of two main parts: the cephalothorax and the abdomen. This bipartite body design plays a vital role in their functionality. For instance, the cephalothorax houses critical organs including the digestive system and eyes, while the abdomen contains reproductive organs and silk glands.
A key characteristic of body structure is its adaptation to various environments. Many California spiders have evolved to possess robust and compact bodies, enabling them to thrive in diverse habitats ranging from forests to urban areas. The unique feature being the flexibility in segment size; larger cephalothoraxes allow for more effective predation, while slimmer abdomens might improve agility in navigating through dense foliage. However, a heavier body can limit speed, presenting both advantages and disadvantages in predatory scenarios.
Color and Markings
Color and markings serve not just for aesthetic purposes. They play a crucial role in camouflage and mimicry, providing essential advantages in California's varied landscapes. The bold stripes on a wolf spider, for example, allow it to blend seamlessly into its environment. This adaptability helps to avoid detection by both predators and prey, underscoring the importance of this characteristic.
In this article, color and markings are highlighted for their vital role in identification. A defining feature is the array of patterns on the Latrodectus hesperus, or Western Black Widow, known for its distinctive red hourglass marking. Such markings can signal toxicity, a critical point for understanding safety around these spiders. However, reliance on color can sometimes lead to misidentification, especially in poorly lit environments.

Leg Features
Legs are crucial not only for locomotion but also for hunting strategies and web construction. In California, the leg structure varies significantly across species. One interesting detail is that some spiders, like the tarantula, have particularly thick and hairy legs. This feature aids in stability and provides sensory feedback for detecting prey and environmental changes.
Legs must be emphasized in this discussion for their role in mobility and effectiveness in predation. A unique aspect is the presence of different leg lengths relative to the spider's habitat; for example, wolf spiders have long legs adapted for quick sprints, while orb-weavers typically have shorter, sturdier legs for web construction. The advantages of these leg features are clear: they enable individualized hunting techniques and help support various lifestyles.
Behavioral Traits
Hunting Strategies
California spiders exhibit a range of hunting strategies, which vary based on species and environmental contexts. Wolf spiders are known for their active hunting approach, roaming their territory to catch their prey. They rely on a keen sense of sight and speed over acute web-building skills, making them interesting for enthusiasts eager to observe predatory behavior firsthand.
The adaptability observed in their hunting strategies is a highlight in this guide. One unique feature is their ability to ambush prey, using environmental cover to their advantage. However, while active hunters might seem dominant, web-building spiders showcase a different set of skills. Predators that use webs often employ a sit-and-wait tactic, which can be more energy-efficient.
Web Construction
Web construction is an architectural marvel that reflects both the skill and species of the spider. California boasts a multitude of web styles, from the classic orb-shaped designs of orb-weavers to the more irregular and tangled webs of cobweb spiders. The techniques involve complex silk production processes that are as fascinating as they are functional.
In this guide, the diversity in web construction methodologies is worth noting. A unique characteristic is the ability to recycle silk, allowing spiders to modify their webs as needed for tailored hunting situations or environmental changes. While constructing a web may require significant energy investment, the potential payoff in capturing prey through a well-designed web is a powerful adaptation. On the flip side, poorly constructed webs can lead to missed opportunities in capturing food.
"Spiders, with their varied adaptions and hunting strategies, demonstrate the complexity of nature at play. Understanding these traits can transform a casual observer into a knowledgeable enthusiast."
Common Spider Families in California
Understanding the common families of spiders in California is crucial for anyone keen on recognizing these fascinating arachnids. This knowledge not only aids in identifying the species but also alleviates misconceptions people may hold regarding spiders. Different families exhibit unique characteristics, behavior, and habitats which contribute to the broader ecological system. By grasping these differences, enthusiasts can appreciate their importance while safely navigating environments where spiders thrive.
Wolf Spiders
Identification Tips
Wolf spiders are distinctive for their robust build and excellent vision. They don’t spin webs but rather hunt their prey on foot. Key characteristics to identify these spiders include the absence of a webbed home and the presence of eight long legs. Their coloration ranges from brown to gray, often housing intricate patterns that help them blend into their surroundings. While their size can vary significantly, adult wolf spiders typically measure between one to two inches.
When looking to identify a wolf spider, pay close attention to their eye arrangement. They possess a unique pattern of eight eyes—two big ones in the center and six smaller ones that sit above and below. This trait can be advantageous when identifying them in the wild.
Hunting Behavior
Wolf spiders are nocturnal hunters. They rely on their keen eyesight rather than silk traps to capture prey. Their style of hunting is often characterized by stealth and speed. They can pounce on their prey with remarkable agility, making them effective predators in the ecosystem. This hunting behavior contributes to the control of pest populations, which is beneficial for local gardens and agricultural practices.
However, their hunting skills make them an enviable species to observe but also necessitate caution among those who might mistake them for more dangerous spiders. Understanding their behavior might help mitigate fears.
Orb-Weavers
Recognizing Distinct Patterns
Orb-weavers are well-known for their beautiful, wheel-shaped webs which serve both as a hunting apparatus and a protective environment. They come in a variety of shapes and colors, aligning with their ability to blend into different environments. Distinct patterns on their abdomen often vary significantly between species. Some might have vibrant reds and yellows while others remain more muted.
These patterns play a crucial role not only in their camouflage but also in attracting mates. Recognizing the unique patterns associated with different species can greatly enhance one’s identification skills. Notably, some orb-weavers will change color through the seasons, adapting to their environment, which is quite unique in the spider world.
Web Types
The webs built by orb-weavers are not just beautiful but scientifically fascinating. They produce different types of silk for various purposes—some for trap-building, others for wrapping prey or creating egg sacs. The designs can range from neat, symmetrical patterns ideal for intercepting flying insects, to irregular shapes which some use for more opportunistic hunting methods.
Their webs are instrumental in filtering and controlling insect populations, thus serving as a natural form of pest control in gardens. However, it’s essential to recognize the difference between these intricate webs and those of potentially harmful spider species that adopt less desirable approaches, ensuring proper understanding of local fauna.
Tarantulas
Size and Color
Tarantulas are among the largest spiders one might encounter in California. Their size can range from four to ten inches, and they exhibit a variety of colors, from earthy brown tones to vibrant blues and greens in some species. Their significant size makes them both intimidating and fascinating. Often seen as gentle giants, these spiders can live for years, sometimes even decades, in appropriate conditions.
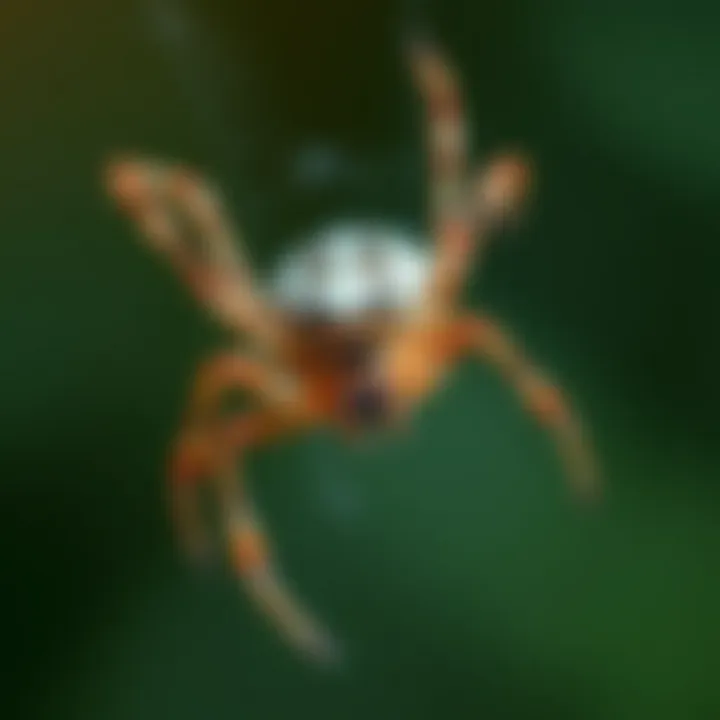


Identifying a tarantula usually involves looking for their robust body and thick legs. The contrast in color often helps distinguishing them in natural landscapes. It’s crucial to note that their size and appearance can evoke fear; however, they are mostly harmless unless provoked.
Habitat Preferences
Tarantulas can be found in a diverse range of habitats, including deserts, forests, and grasslands. They generally prefer burrowing environments, creating homes deep within the substrate. Their preference for such habitats aligns with their lifestyle as ground-dwelling hunters. Understanding these habitat preferences aids in predicting their whereabouts during certain seasons.
During the warmer months, they are more active, often venturing out at night in search of mates or prey. This aspect is important for those who wish to observe them in nature while ensuring they are not disturbed. Recognizing where they thrive can also help individuals avoid unintentional encounters.
Black Widows
Toxicity and Safety
The black widow is infamous for its venomous bite, making it one of California's most recognized spiders. It's critical to approach this species with respect. Their glossy black bodies and the distinctive red hourglass marking on the underside of their abdomens are pivotal for proper identification. Understanding the risks associated with them can help dispel unnecessary fears while simultaneously promoting safe practices when encountering them.
Their bites can have serious consequences, especially for those with weakened immune systems, making knowledge about their presence essential for safety. However, many bites occur due to accidental encounters—hence the importance of awareness.
Identification Methods
Identifying a black widow can often be straightforward if one is aware of their key characteristics. Aside from color and shape, one should also familiarize themselves with their typical habitats, often secluded areas like wood piles or underbrush. Recognizing common signs of their presence can help mitigate unwanted encounters.
An effective method for identification includes the careful observation of web structure. Black widow webs are irregular and often messy, differing significantly from the neatly constructed webs of orb-weavers. Additionally, other online resources, such as educational websites and local wildlife databases, can further support accurate identification efforts and contribute to safer outdoor experiences.
Seasonal Variations in Spider Activity
Understanding the seasonal variations in spider activity is crucial for both enthusiasts and researchers alike. Different seasons bring about distinct behaviors in spiders, significantly impacting their lifecycle events such as mating, feeding, and survival strategies. By recognizing these patterns, one can better appreciate the adaptability of spiders to changing environments and their role in local ecosystems.
Spring and Summer
During spring and summer, the world comes alive, and so do the spiders. These warmer months kick-start the breeding habits of many species in California.
Breeding Habits
Breeding in spiders is often a complex affair. Female spiders are usually the stars of the show, attracting males with pheromones. This selective process not only aids in genetic diversity but also promotes the survival of the fittest. By identifying breeding patterns, one can gauge the health of local spider populations. A prominent aspect of breeding habits is courtship displays, which vary widely among species; some might involve intricate dances or specialized web formations.
Each unique approach can provide critical insights into environmental shifts. For instance, if a spider species typically known for its elaborate courtship suddenly changes its behavior, it might signal ecological stresses. Thus, understanding these habits is not just fascinating; it’s an essential tool for monitoring ecological health.
Feeding Patterns
As the season heats up, so does the competition for food. Spider feeding patterns shift dramatically in response to the abundance of prey. During spring and summer, spiders actively hunt and trap insects, which are plentiful. Their diets often consist of flies, mosquitoes, and moths, sometimes turning to even larger creatures when they have the opportunity.
A key characteristic here is the method of hunting. Some spiders, like the orb-weavers, will spin vast webs to ensnare prey, while others, like wolf spiders, rely on stealth and speed to capture their meals. This diversity in feeding strategies reflects the adaptability of spiders. Watching how these feeding behaviors adjust according to the available food sources can provide a deeper understanding of the ecological dynamics at play.
Fall and Winter
As the temperatures drop, spiders begin to prepare for the cooler months ahead, changing their behaviors considerably.
Hibernation Behaviors
When winter rolls around, many spiders exhibit fascinating hibernation behaviors. Some enter a state akin to dormancy, slowing down their metabolic rate to survive the harsh conditions. This hibernation tactic allows spiders to conserve energy until the warmth of spring returns.
Different species employ varying strategies—some might find a sheltered crevice, while others might remain within the confines of their webs. Notably, a unique feature of this behavior is that not all spiders hibernate; species like the tarantula can remain active but will seek out warmer microclimates.
Understanding these behaviors sheds light on how spiders endure challenging conditions, thus reinforcing their role in the ecosystem even in adversity.
Nesting Arrangements
Nesting arrangements change with the seasons, greatly impacting the survival of spider offspring. In the fall, many spiders will prepare their homes for winter. Some females construct egg sacs containing dozens or hundreds of eggs, which they might guard until the offspring hatch out in spring. This aspect of their lifecycle is particularly fascinating as it highlights the resource investment spiders make in their young.
Each species has its own nuances; some will create silken retreats while others may depend solely on their environment for protection. Understanding these nesting arrangements can provide insight into how species persist in varying climates and what adaptations they develop as a response to environmental pressures.


"By observing the cyclical patterns of spider activity, we gain not just an appreciation for these creatures, but also a deeper understanding of the ecosystems they inhabit."
By studying the seasonal variations in spider activity, one can enhance their knowledge of each species' lifecycle, contributing to their overall conservation and appreciation in California.
Methods for Correctly Identifying Spiders
Identifying spiders accurately is important for fostering both appreciation and understanding of these creatures. Misidentification can lead to unnecessary panic or the incorrect assumption of danger. Correctly identifying spiders can shed light on their roles in local ecosystems and guide appropriate interaction. Not only can it inform you on how to handle them safely, but understanding spider types can also help gardeners optimize their pest control methods.
Field Guides and Resources
Recommended Books
When it comes to identifying spiders, field guides are invaluable. They often contain photographs, illustrations, and descriptions that make identification straightforward. A widely recommended resource is "Spiders of California" by Richard S. Vetter. This book is known for its clear imagery and comprehensive descriptions of species common to the state. The key characteristic that stands out in this work is the inclusion of habitat information which is essential for anyone looking to find spiders in their natural environments.
However, while books can provide detailed information, they often lack the interactivity that some might prefer. Additionally, they may not always stay current with recent discoveries or classifications, which can be crucial for enthusiasts aiming for high accuracy.
Online Databases
On the other hand, online databases such as the California Academy of Sciences' biodiversity portal offer real-time updates and a vast range of species catalogs. These databases provide an interactive experience with filters to help narrow down searches based on specific characteristics. The dynamic nature of these resources makes them beneficial for enthusiasts who want the latest information.
Yet, the vast array of data can sometimes overwhelm users, and reliability varies based on contributor expertise. It’s essential to cross-check findings with reputable sources to avoid relying on inaccurate information.
Photography Techniques
Capturing Detailed Images
Taking high-quality images can enhance your identification process significantly. Good photography allows for close examination of features like markings, body size, and leg structure. Using a macro lens can make a world of difference. Focus on clarity and detail; this is where quality reigns. People often underestimate the power of good visuals while identifying species.
One preferred method involves using natural light to avoid flash glare, which can obscure details. However, keep in mind that natural light changes throughout the day, affecting your best photography time. In circumstances where detail is essential, dedicating time for proper lighting can yield vastly superior images.
Using Software for Identification
In the digital age, utilizing software apps for species identification is becoming increasingly popular. Programs like Seek by iNaturalist and Picture Insect allow users to identify spiders by simply snapping a picture. These applications employ advanced algorithms that compare your image against a large database of spider images.
A notable advantage of these tools is their accessibility; you could have a wealth of knowledge at your fingertips anytime. However, such identifications might not always be completely accurate, particularly for novice users who may misinterpret the results. Combining images with other identification methods ensures more reliable outcomes.
Using both offline books and online tools creates a balanced approach to spider identification, combining traditional knowledge with modern technology.
Safe Handling and Conservation Practices
When engaging with spiders in California, it’s crucial to understand not just how to identify them but also how to interact with and respect their roles in our ecosystem. Safe handling practices are paramount to ensure both your safety and the welfare of the spiders. Additionally, promoting spider conservation efforts helps maintain biodiversity and ecological balance. By being informed and cautious, enthusiasts can enjoy learning about these fascinating creatures while minimizing potential risks and contributing to their preservation.
Avoiding Bites and Allergic Reactions
Protective Gear
One cannot emphasize enough the significance of wearing protective gear when handling spiders. Gloves are perhaps the most fundamental aspect of this kind of protection. They not only provide a barrier between your skin and any potential spider bites but also help you feel more confident when you are close to spiders. Thick fabric gloves can shield your hands from sharp legs and can also help when dealing with webs, which may be more fragile than they appear. However, one should not rely solely on gloves, as the type of gloves can affect one's dexterity while handling.*
- Additionally, wearing long sleeves and durable pants can protect your arms and legs from unexpected encounters, as certain species tend to be more defensive.
Recognizing Signs of Distress
Being able to recognize signs of distress in spiders is crucial for both your safety and the spider’s wellbeing. When a spider feels threatened, it may display various defensive behaviors. For instance, a tarantula may raise its front legs and display its fangs, indicating it’s ready to defend itself. Understanding these signals can help you avoid provoking the spider, creating a safer interaction overall. This awareness is not just beneficial for you; it also ensures that the spider remains undisturbed and is less likely to behave aggressively, which is crucial for conservation efforts. Misinterpretation of these signs can lead to unnecessary harm to these arachnids.
Promoting Spider Conservation
Creating Spider-Friendly Environments
Creating environments that are welcoming to spiders is a vital aspect of conservation. This can involve allowing for some natural cover in gardens, like leaving debris or letting certain plants grow wild, since these environments offer ideal habitats for spiders. Further, having a balanced ecosystem in your backyard encourages spiders to thrive, which adds to biodiversity. An added advantage is that spiders play a role in pest control; hence, a spider-friendly garden often requires less chemical intervention, benefiting both the environment and your plants.
Participating in Citizen Science
Engaging the community through citizen science can immensely aid spider conservation. Initiatives that encourage people to report spider sightings or collect data on different species help in understanding their populations and distributions. Such collective efforts contribute to scientific research and heighten awareness of spider ecology among the public. Furthermore, these activities foster a connection between local communities and their natural surroundings, encouraging an appreciation for biodiversity. Plus, seeing the impact of your contributions can be quite rewarding.
"The continued existence of spiders, as well as other creatures, relies on our choices today; the more we learn, the better equipped we are to make impactful decisions on their behalf."
By actively participating in spider conservation through mindful practices and community engagement, we can pave the way for a healthier ecosystem. Understanding how to handle these creatures safely while promoting their well-being can lead to richer interactions and deeper respect for their lives in the wild.















